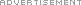Collagen Injections – Benefits, Cost & Side Effects
Reviewed by Mitchel Goldman, MD
Collagen injections may help erase frown lines, “crow’s feet” and nasolabial folds or smile lines. Collagen injections have been around for a while, but have decreased in popularity with the introduction of soft tissue fillers such as Restylane, which can last longer.
In 2007, there were 174,290 collagen injections performed in the United States, down about 70 percent from 2000, according to statistics compiled by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons
What Are Collagen Injections, and How Do They Work?
Collagen is the main protein found in connective tissue. It supports the skin, bone, cartilage and blood vessels. Collagen composes up to 80 percent of the skin. Its role is to maintain the skin’s integrity, but collagen breaks down with advancing age. The breakdown of collagen during the aging process can lead to wrinkles, lines and folds. Collagen injections replenish the skin’s natural collagen.
Several types of Collagen fillers are on the market. For example, collagen fillers containing human collagen include CosmoDerm and Cosmoplast. Cow (bovine) collagen fillers include Zyderm and Zyplast. Bellafill is a hybrid gel filler consisting of millions of synthetic microspheres (polymethylmethacrylate or PMMA) suspended in purified bovine (cow) collagen.
Ideal Candidates for Collagen Injections
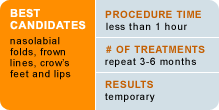
Optimal candidates for collagen injections are typically between the ages of 35 and 60 with frown lines, “crow’s feet” and nasolabial folds or smile lines.
People who should not receive collagen injections include those who are pregnant or nursing, people with allergies to cow products or lidocaine, or those with certain medical conditions such as autoimmune diseases.
The Collagen Injection Procedure
Zyderm and Zyplast do require a skin test prior to the first treatment because of the risk of allergic reaction in some people.
Collagen injections are typically performed in the doctor’s office. They are most often performed without anesthesia, although the collagen filler itself contains lidocaine, which is a local anesthetic. Collagen is injected with a tiny needle into the skin depressions. Several injections may be needed, depending on the length and depth of the wrinkle. The procedure takes less than an hour.
The points of injection are “scored” by the doctor with a pencil. Your doctor may select numerous injection points for each location slated for treatment. Antiseptic is also applied. Your doctor will then decide on the correct amount of collagen to be used. The collagen filler is injected into the marked points beneath the skin.
Recovery After Collagen Injections
You may experience some minimal discomfort from the collagen injection. There may be some swelling and bruising, which typically subsides within 48 hours. The treated area may look red for the first 24 hours, and this may last up to a week.
You can go home shortly after the procedure. The results are immediate and become fully evident within one week. In some cases, the treated area may appear to be overfilled initially. However, this will dissipate soon after to produce a more natural-looking appearance. Results may be unpredictable, lasting from two to three months.
You can resume normal activities immediately; however, it is advisable to stay out of the sun. Tell your doctor about any unmanageable pain or symptoms that are progressive or abnormal.
Complications and Risks of Collagen Injections
Complications from collagen fillers are typically minimal. Some possible complications include uneven texture of the skin, an allergic reaction, infection, abscess and scarring.
Alternative and Additional Treatments
While collagen is a good option, it is always a good idea to investigate alternative treatments. Other minimally invasive procedures include Botox, which may be complementary to collagen, or Restylane, which may be a better substitute for collagen. For more severe conditions, surgical procedures may be more appropriate, such as a facelift, forehead lift (brow lift) and blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery).
Your doctor may recommend additional treatments for you to consider in conjunction with collagen, such as a chemical peel, laser skin resurfacing, or microdermabrasion.
Consult a Qualified Doctor
Dermatologists and plastic surgeons may have extensive knowledge of and experience with collagen injections. However, some may not have expertise with selecting accurate injection points and proper dosage; or have familiarity with both human-based and bovine-based collagen fillers. Finding a doctor with specific experience in these areas is important for achieving optimal results for your condition.
Here are some tips to consider when consulting a doctor:
- Review the doctor’s credentials, education, training, type of certification held and number of times that he or she has performed the treatment.
- Request information about the type of filler recommended, bovine-based or human-based collagen. If the doctor is using a bovine-based collagen filler, he or she will perform an allergy test that requires four weeks of review in order to ensure that you won’t have an allergic reaction. If the test rules out allergies, the bovine-based collagen filler can be used. Human-based collagen filler does not require an allergy test.
- View before-and-after photos of patients with similar conditions who received collagen fillers and alternative procedures such as Restylane.
- Inquire about complication risks and possible side effects.
- Ask the doctor to estimate the number of treatments required to achieve and maintain the results you are looking for.
- Request a list of pre-op and post-op instructions. Following these instructions can reduce the risk of complications.
- Inquire about how long the procedure will last
The Cost of Collagen Injections
The cost for collagen fillers can range from $300 to $400 per syringe. Some people require more than one syringe. The total procedure costs may be up to $700.
Purely cosmetic procedures are not covered by insurance. If the cost is higher than you can pay at once, ask your surgeon about monthly payments.
About the Reviewer of This Article
Mitchel P. Goldman, MD, is certified by the American Board of Dermatology and a fellow of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery focusing on phlebology (the study of veins), laser surgery and liposuction. Dr. Goldman received his medical degree from Stanford University School of Medicine and dermatology specialty training at the University of California, Los Angeles. He maintains hospital staff privileges at Scripps Hospital and the VA Medical Center, both in La Jolla, Calif., where he practices, and is a volunteer clinical professor of dermatology/medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He is an associate editor of Dermatologic Surgeryand The Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology and has authored more than 300 medical articles.